New York City Agar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The NYC (
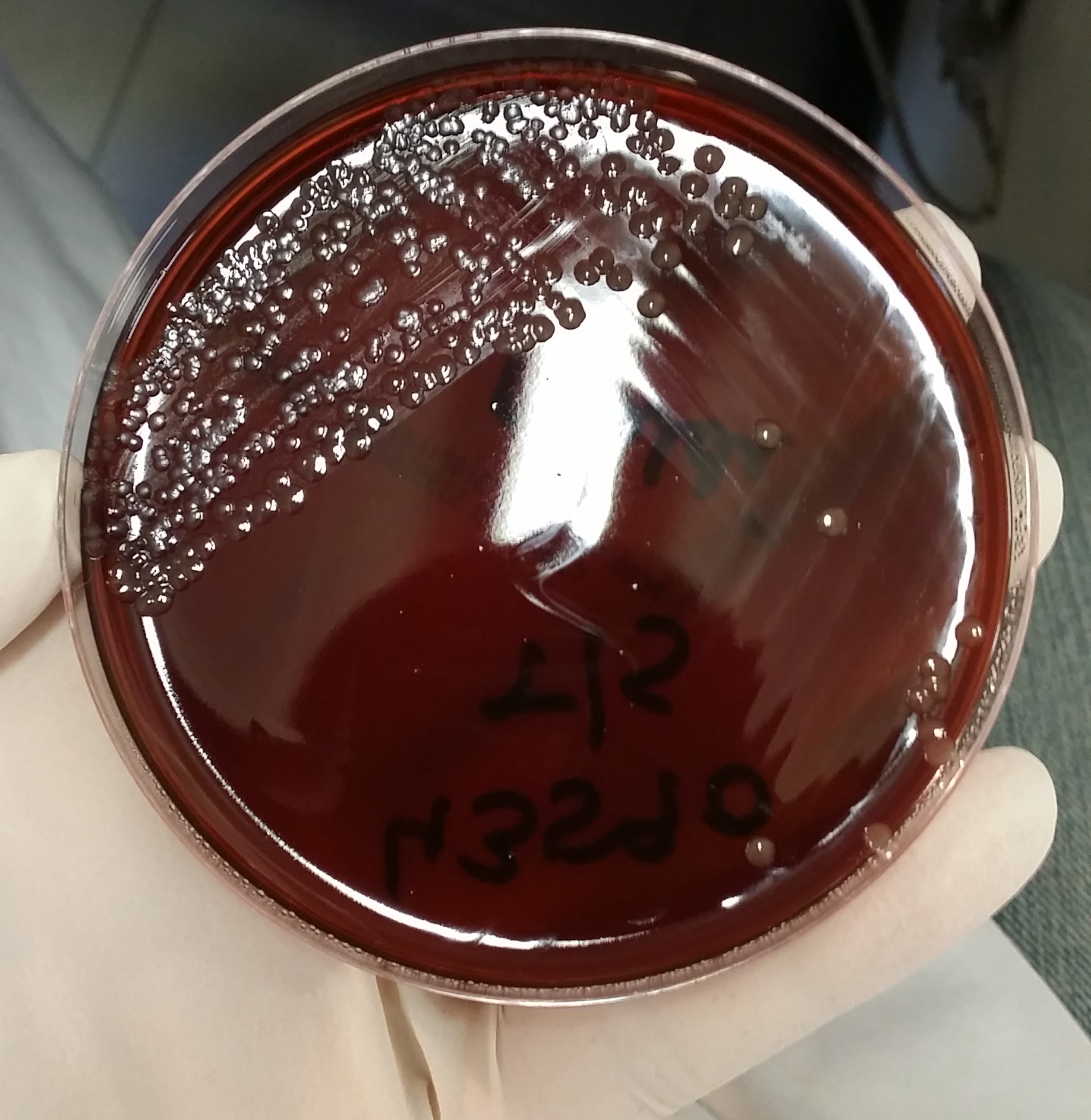 Streak the specimen as soon as possible after it is received in the
Streak the specimen as soon as possible after it is received in the
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
) medium or GC ('' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'') medium agar is used for isolating Gonococci.Fauer, Weisburd, Wilson and May, 1973, Health Lab. Sci., 10: 44.
Composition
The agar base is composed of: ''Final pH ( at 25°C) 7.4±0.2''Background and principles
NYC Agar Base was originally developed by Fauer, Weisburd and WilsonFauer, Weisburd and Wilson, 1973, Health Lab. Sci., 10: 55. at theNew York City Department of Health
The New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene is the department of the government of New York City responsible for public health along with issuing birth certificates, dog licenses, and conducting restaurant inspection and enforcem ...
for selective isolation of pathogenic ''Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, '' N. meningitidis'' and ''N. gonorrhoeae''.
''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negativ ...
'' species from clinical specimens. It consists of primarily a peptone-corn starch agar-base buffered with phosphates
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
and supplemented with horse plasma, horse haemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
, dextrose, yeast autolysate and antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
. This medium is superior to other media generally employed for the isolation of ''Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, '' N. meningitidis'' and ''N. gonorrhoeae''.
''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negativ ...
'' species. The transparent nature of the medium helps in studying the colonial types.
Proteose peptone, horse plasma, haemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ...
provide nutrients for the growth of '' N. gonorrhoeae'' and '' N. meningitidis''. Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
buffers the medium. The selective supplement added contains the antibiotics vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, ...
, colistin
Colistin, also known as polymyxin E, is an antibiotic medication used as a last-resort treatment for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections including pneumonia. These may involve bacteria such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Klebsiella ...
, nystatin
Nystatin, sold under the brandname Mycostatin among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat '' Candida'' infections of the skin including diaper rash, thrush, esophageal candidiasis, and vaginal yeast infections. It may also be ...
and trimethoprim
Trimethoprim (TMP) is an antibiotic used mainly in the treatment of bladder infections. Other uses include for middle ear infections and travelers' diarrhea. With sulfamethoxazole or dapsone it may be used for ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia in peo ...
, to suppress the accompanying flora. Vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, ...
is inhibitory for gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bact ...
bacteria. Colistin
Colistin, also known as polymyxin E, is an antibiotic medication used as a last-resort treatment for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections including pneumonia. These may involve bacteria such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Klebsiella ...
inhibits gram negative
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one one thousandth of a kilogram.
Originally defined as of 1795 as "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to th ...
bacteria, including ''Pseudomonas species'', while Proteus
In Greek mythology, Proteus (; Ancient Greek: Πρωτεύς, ''Prōteus'') is an early prophetic sea-god or god of rivers and oceanic bodies of water, one of several deities whom Homer calls the "Old Man of the Sea" ''(hálios gérôn)''. ...
is inhibited by trimethoprim
Trimethoprim (TMP) is an antibiotic used mainly in the treatment of bladder infections. Other uses include for middle ear infections and travelers' diarrhea. With sulfamethoxazole or dapsone it may be used for ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia in peo ...
.Knapp and Koumans. 1999. In Murray, Baron, Pfaller, Tenover and Yolken (ed.), Manual of clinical microbiology, 7th ed. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C The combination of trimethoprim
Trimethoprim (TMP) is an antibiotic used mainly in the treatment of bladder infections. Other uses include for middle ear infections and travelers' diarrhea. With sulfamethoxazole or dapsone it may be used for ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia in peo ...
and colistin
Colistin, also known as polymyxin E, is an antibiotic medication used as a last-resort treatment for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections including pneumonia. These may involve bacteria such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Klebsiella ...
acts synergistically
Synergy is an interaction or cooperation giving rise to a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts. The term ''synergy'' comes from the Attic Greek word συνεργία ' from ', , meaning "working together".
History
In Christia ...
against gram-negative bacilli. Starch neutralizes the toxic metabolites produced by ''Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, '' N. meningitidis'' and ''N. gonorrhoeae''.
''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negativ ...
''. The yeast autolysate supplement fulfils the requirements needed to enhance ''Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, '' N. meningitidis'' and ''N. gonorrhoeae''.
''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negativ ...
'' growth. Yeast contains oxaloacetic acid
Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes ...
which is metabolized by gonococci to produce sufficient for growth of capnophilic gonococci. Also, presence of yeast autolysate reduces the lag phase
250px, Growth is shown as ''L'' = log(numbers) where numbers is the number of colony forming units per ml, versus ''T'' (time.)
Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing ...
of growth of ''Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, '' N. meningitidis'' and ''N. gonorrhoeae''.
''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negativ ...
'', thus enhancing both size and number of colonies. The specimen can be directly streaked on the medium to obtain maximum isolation.
Procedure
 Streak the specimen as soon as possible after it is received in the
Streak the specimen as soon as possible after it is received in the laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physic ...
. If material is being cultured directly from a swab, proceed as follows:Center for Disease Control. 1975. Criteria and techniques for the diagnosis of gonorrhea, USPHS, Atlanta, Ga.
# Roll swab directly on the medium in a large “Z” to provide adequate exposure of swab to the medium
Medium may refer to:
Science and technology
Aviation
*Medium bomber, a class of war plane
*Tecma Medium, a French hang glider design
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to store and deliver information or data
* Medium of ...
for transfer of organisms
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
.
# Cross-streak the “Z” pattern with a sterile wire loop, preferably in the clinic
A clinic (or outpatient clinic or ambulatory care clinic) is a health facility that is primarily focused on the care of outpatients. Clinics can be privately operated or publicly managed and funded. They typically cover the primary care needs ...
. If not done previously, cross-streaking should be done in the laboratory.
# Place the culture as soon as possible in an aerobic
Aerobic means "requiring air," in which "air" usually means oxygen.
Aerobic may also refer to
* Aerobic exercise, prolonged exercise of moderate intensity
* Aerobics, a form of aerobic exercise
* Aerobic respiration, the aerobic process of cel ...
environment enriched with carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
.
# Incubate at 35 ± 2 °C and examine after overnight incubation and again after approximately 48 hours.
# Subculture for identification of '' N. gonorrhoeae'' should be made within 18–24 hours. If shipped after incubation, colonies should be subcultured before performing biochemical identification tests in order to ensure that adequate viability is achieved.
Expected results
Typical colonial morphology is as follows: '' N. gonorrhoeae'' may appear as small (0.5–1.0 mm) grayish white to colorless mucoid colonies. '' N. meningitidis'' appears as large colorless to bluish-gray mucoid colonies. Colonies may be selected for Gram-staining, subculturing or other diagnostic procedures.References
{{Growth media Microbiology Microbiological media Cell culture media